Article No. VK-PHY09
PHY09 Ultrasonic computer tomography (CT)
Demonstration of the formation of an ultrasonic CT scan
- Subject matter of the experiment
- Theoretical and practical aspects of the experiment
- Results
- Equipment
- Related Experiments
In this experiment the formation of an ultrasonic CT scan image is clearly shown. The relevance and differences of individual measurement parameters such as attenuation and sound velocity are analysed and the influence of filters and image processing is investigated.
Keywords: Reflection, scattering, transmission, absorption, acoustic attenuation, sound velocity, resolution, ultrasonic echography (A-Scan, B-Scan), tomography, CT scan image, image processing, filters
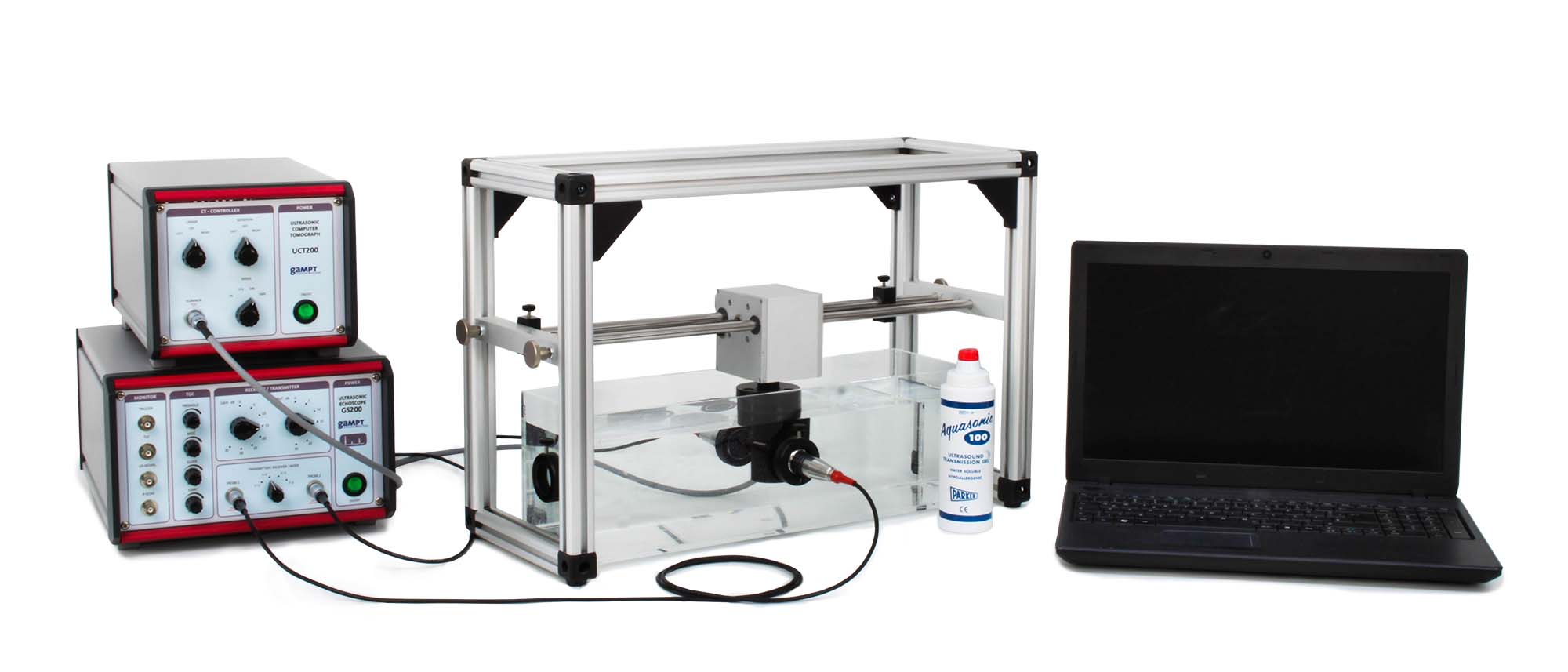
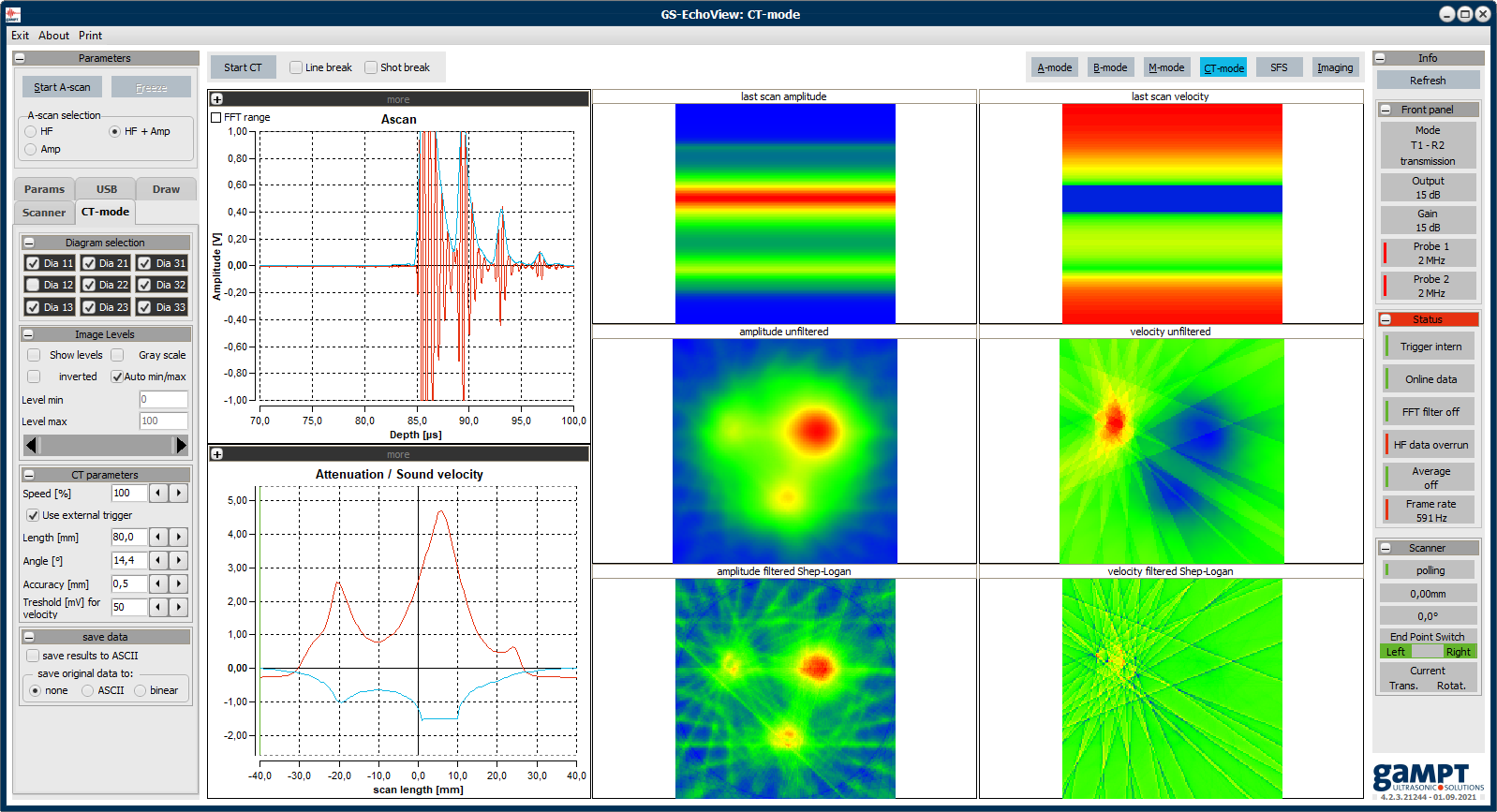
X-ray CT, MRT and PET are computer-aided imaging methods used in medical diagnostics, industry and research. Processes such as radiation absorption, nuclear magnetic resonance or particle emission are used to produce cross-sectional images by means of appropriately measurable physical quantities. Ultrasonic computer tomography is another CT method. It differs from X-ray CT in that instead of the attenuation of X-rays, the attenuation and times of flight of ultrasonic signals in the test object are measured. With our ultrasonic CT, line scans are recorded at different angles and put together to form a cross-sectional image. In this process, the sample arranged between transmission and receiving probe is moved and turned under computer control. The overlaying of the projections of individual scans can be followed step by step on the PC.
In the experiment, the process of generating an ultrasound computer tomogram (ultrasound measurement > projection > back projection > tomogram) is traced step by step. Sound attenuation and sound velocity tomograms for different settings of transmission power and gain are recorded and analyzed.
Using the Shepp-Logan filter, the use of a filtering algorithm to improve the image quality of CT images is discussed. By changing the parameters for the scaling of the color or gray values, a simple image processing can be performed to change the brightness, contrast, and color of the CT images.
| Ord.no. | Description |
|---|---|
| 10400 | Ultrasonic echoscope GS200 |
| 10152 | 2 ultrasonic probes 2 MHz |
| 60200 | CT scanner |
| 60210 | CT control unit |
| 60121 | CT sample |
| 60124 | CT sample holder |
| 60120 | CT reservoir |
| 70200 | Ultrasonic gel |